Before we get into the wonderful space of biomes, let’s learn about the different terms. Biomes, ecosystems and habitats are words that are frequently confused and used as synonyms, however, they are not:
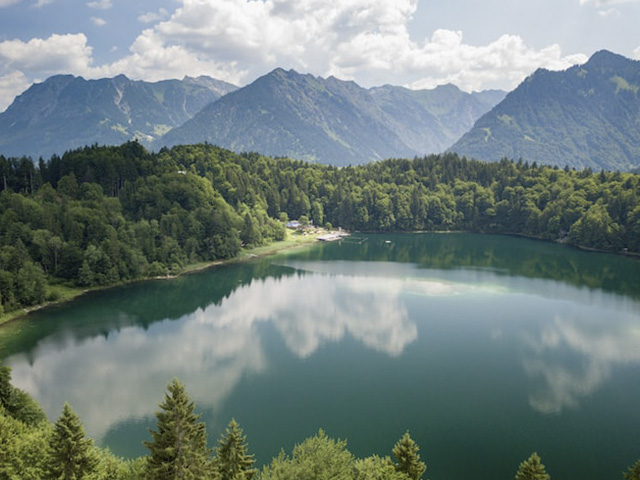
biome: It is an area of the planet that has in common the climate, flora and fauna. It could be defined by its main characteristics (climate, geology and living organisms), and not how they interact with each other.
ecosystem: It is a system composed of living organisms and their interaction with the environment that surrounds them. Unlike the biome, the main focus of the ecosystem is the interaction and relationships between species and the abiotic environment. While in a biome it is more important which species inhabit it and where in the world they are found, in an ecosystem the main issue is how those species interact with each other and with the surrounding environment.
habitat: It is the environment that presents the adequate conditions for an individual, population or species to inhabit. Habitat is primarily focused on a species, a population of a species, or even a single individual. To describe the habitat of a species or individual, the starting point is the individual itself, and then everything that surrounds it is defined.
environment: The environment that includes the conditions of natural physical elements, economic, cultural, political, educational, business, medical, social, etc. of a group, sector, place or time